



Next: Sequential Simulation, Single-Variable Case
Up: Algorithms
Previous: Linear Combination
Subsections
Multi Linear Combination
template<class InputIterator, class InputIterator2>
double
multi_linear_combination(InputIterator begin_weights, InputIterator end_weights,
InputIterator2 first_neigh, InputIterator2 last_neigh)
Computes the linear combination of the weights in range
[begin_weights, end_weights) and the property values of the geo-values contained in the neighborhoods in range [first_neigh, last_neigh). Denote
 ,...,
,...,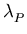 the weights, and
zj(
the weights, and
zj(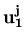 ),..., zj(
),..., zj(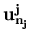 ),
j = 1,..., Nv property values of the geo-values contained in the Nv neighborhoods. linear_combination returns:
where
),
j = 1,..., Nv property values of the geo-values contained in the Nv neighborhoods. linear_combination returns:
where
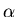 (i, j) =
(i, j) = 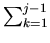 nk + i
nk + i
In header file <kriging.h>
P, the number of weights, must be equal or greater than the total number of geo-values in all the neighborhoods combined.
The algorithm loops on the geo-values, hence if P > N only the N first weights are used, the others are ignored.
The type of the geo-values properties must be convertible to double.
- InputIterator is a model of Input Iterator (see STL). The dereference type of the iterator must be convertible to double.
- InputIterator2 is a model of Input Iterator (see STL). It iterates on a range of Neighborhood
Compute the kriging estimate from the kriging weights. gauss_covariance is the Gaussian covariance defined in the example following the description of kriging_weights.
int main()
{
location2d u1(2,3);
location2d u2(4,-7);
geo_value2d Z1(u1,0.21);
geo_value2d Z2(u2,0.09);
Neighborhood neighbors1, neighbors2;
neighbors1.push_back(Z1);
neighbors1.push_back(Z2);
location2d u3(1,2);
geo_value2d S1(u3,42.1);
neighbors2.push_back(S1);
neighborhood* neigh_array[2]={&neighbors1, &neighbors2};
location2d u(0,0);
std::vector<double> weights;
double kvariance;
kriging_weights(weights, kvariance,
u, neigh_array, 2,
LMC_covariance, OK_constraint);
double kmean = multi_linear_combine(weights.begin(),
weights.end(),
neigh_array, neigh_array+2);
}




Next: Sequential Simulation, Single-Variable Case
Up: Algorithms
Previous: Linear Combination
nicolas
2002-05-07